Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- 벌크연산
- LIST
- 페이징
- joinfetch
- paging
- JPQL
- 대량쿼리
- javaservlet
- jQueryUI
- 제네릭
- jQuery값전달
- 프로젝트생성
- jQuery값전송
- springflow
- 스프링데이터흐름
- Generic
- fetchjoin
- 페치조인
- Hibernate
- namedQuery
- JQuery
- values()
- calendar
- JPA
- 엔티티직접사용
- fullcalendar
- 자바서블릿
- jscalendar
- javascriptcalendar
- 제너릭
Archives
- Today
- Total
가자공부하러!
Spring Security(2) - 전체 구조와 필터 별 역할 정리 본문
섹션2 스프링 시큐리티 주요 아키텍처
1. 위임 필터 및 필터 빈 초기화 - DelegatingFilterProxy, FilterChainProxy
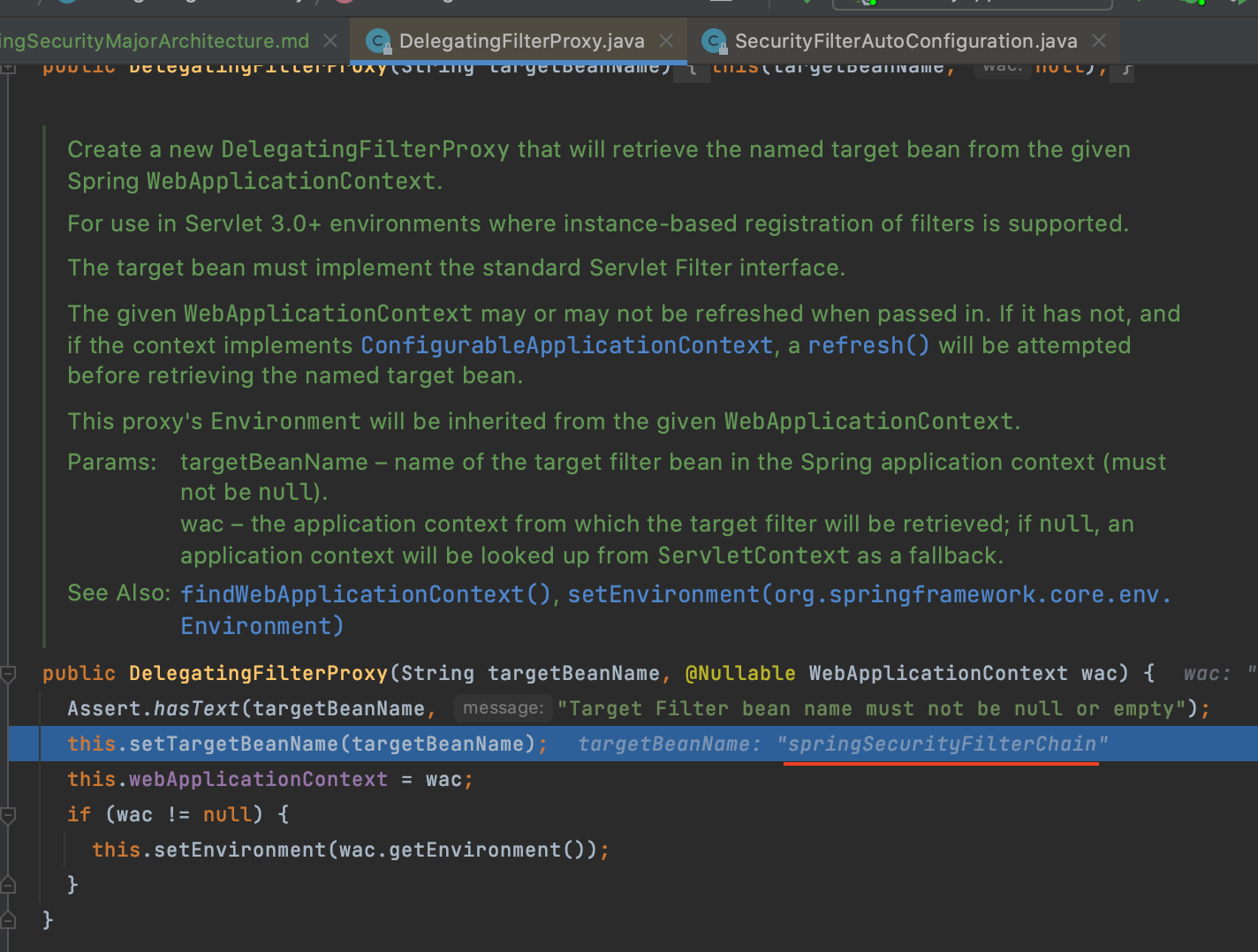
- DelegatingFilterProxy
- ServletFilter
- servlet 스펙 2.3부터 도입됨. servlet으로 요청이 들어가기 전, 후에 동작
- servlet 컨테이너가 만들고 관리
- 스프링에서 만든 내용을 주입받아 사용할 수 없음
- DelegatingFilterProxy
- servlet 필터를 거친 요청을 Spring Bean에 위임시키는 역할
- servlet컨테이너가 초기화될 때 servletFilter로 등록됨
- ApplicationContext에서 springSecurityFilterChain을 찾아 보안처리 위임
- ServletFilter
- FilterChainProxy
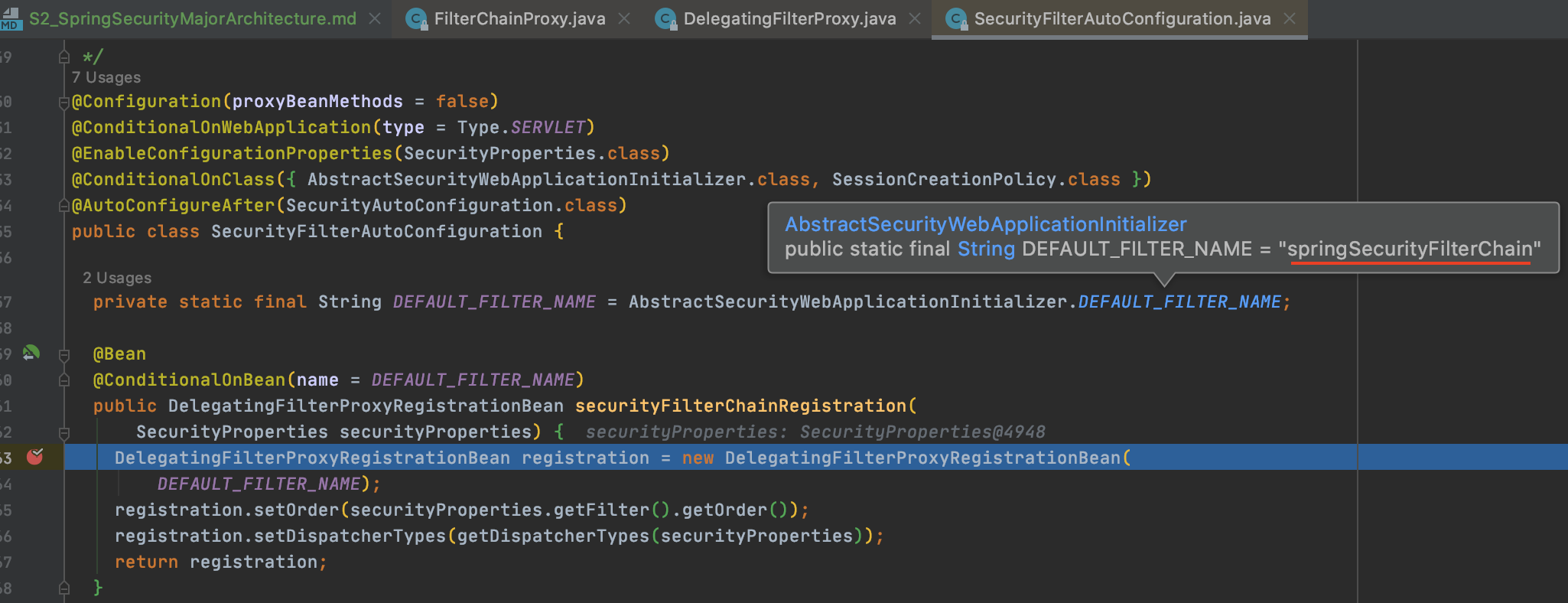
- springSecurityFilterChain이름으로 생성되는 스프링 빈
- 스프링 시큐리티가 초기화될 때 관리할 필터들을 결정(기본필터 + 설정을 통한 추가필터)
- 필터를 순서대로 호출해서 사용자 요청을 각각의 필터에 전달
- 마지막 필터까지 예외가 발생하지 않으면 인증 통과
- 순서 정리
순서
1. 서블릿 컨테이너 초기화할 때 SpringSecurity의 DelegatingFilterProxy를 서블릿 필터로 등록 2. ApplicationContext 초기화 될 때 springSecurityFilterChain 이름으로 설정된 securityFilter들을 가진 FilterChainProxy 등록 3. 서블릿 request가 들어오면 서블릿은 DelegatingFilterProxy를 통해 FilterChainProxy로 request를 보내 보안작업을 위임시킴 4. FilterChainProxy는 보안 작업을 수행 5. 보안 작업이 완료되면 서버로 요청 전달(DispatherServlet)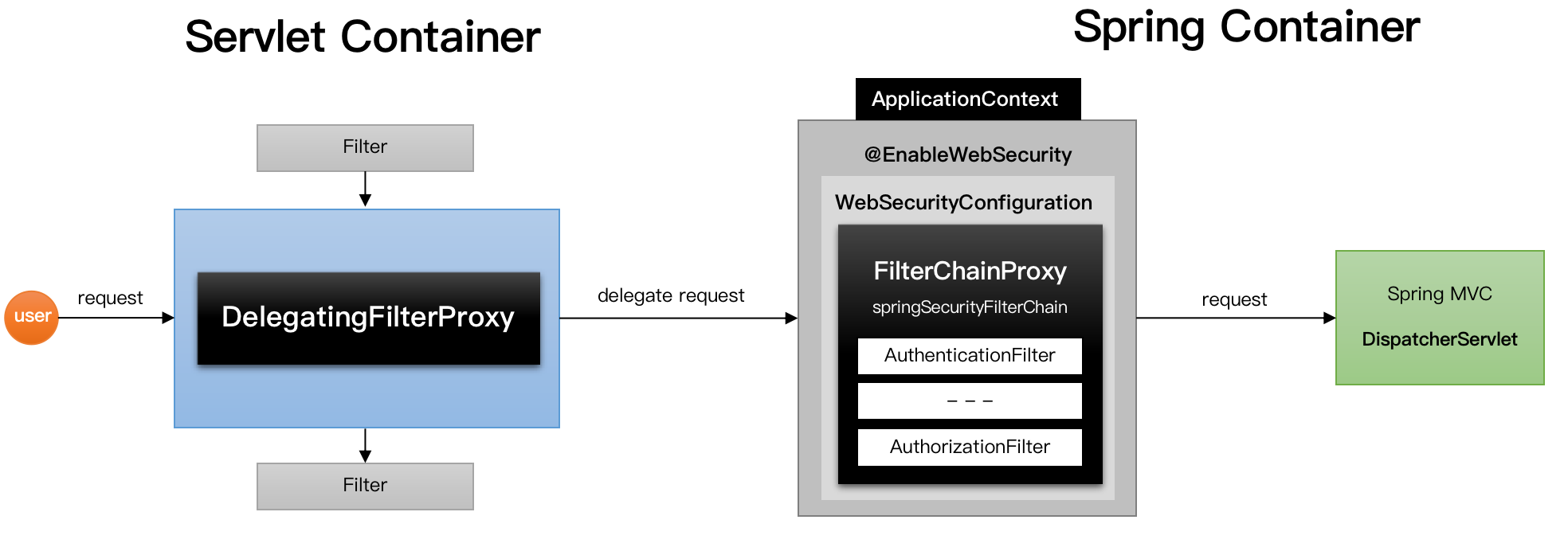
서블릿 필터에서 springSecurityFilterChain이름을 찾을 수 있도록 설정하는 코드
스프링 컨테이너에 FilterChainProxy가 springSecurityFilterChain이름으로 등록되는 코드
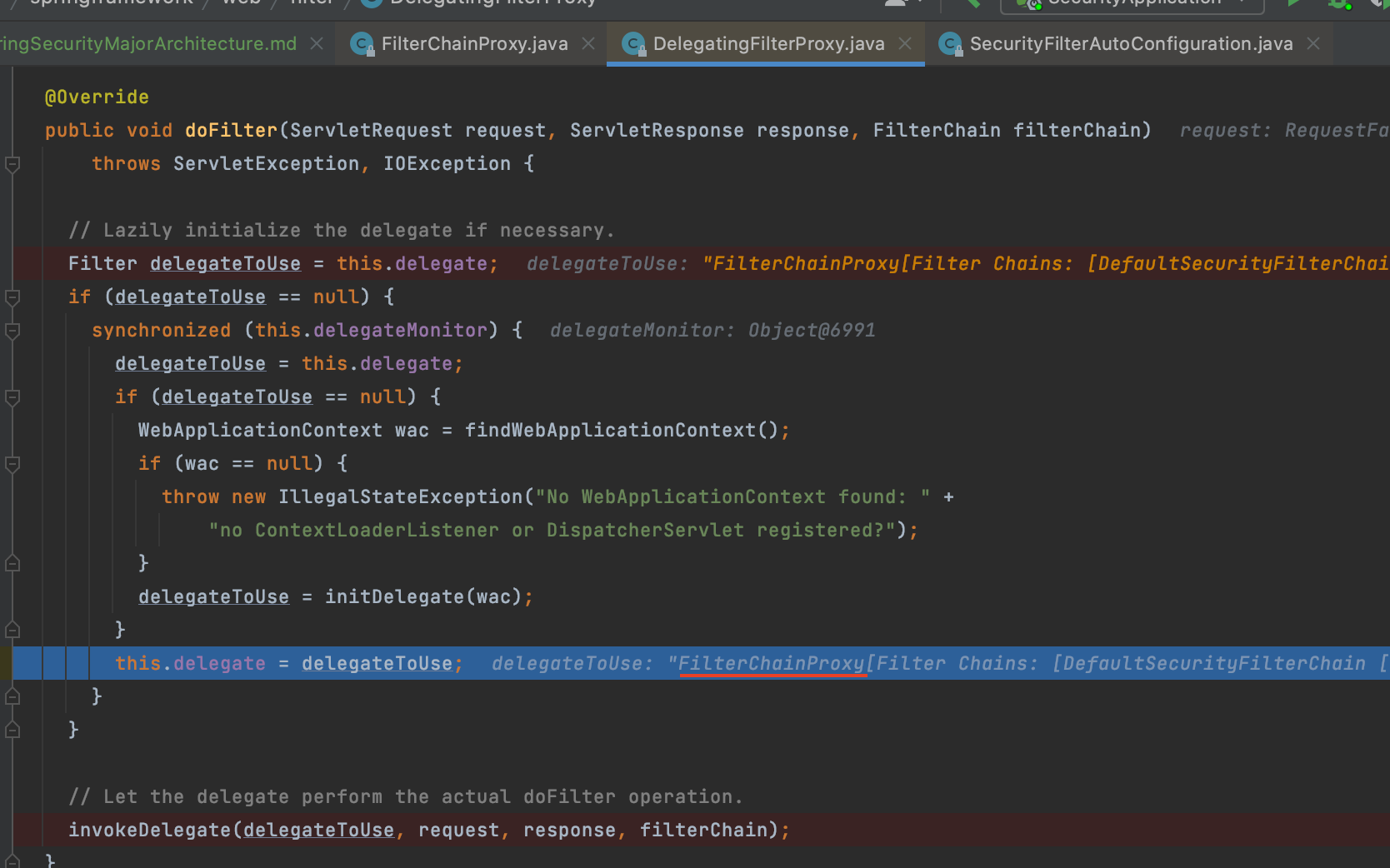
DelegatingFilterProxy가 springSecurityFilterChain을 찾고 그 필터에게 위임하는 동작
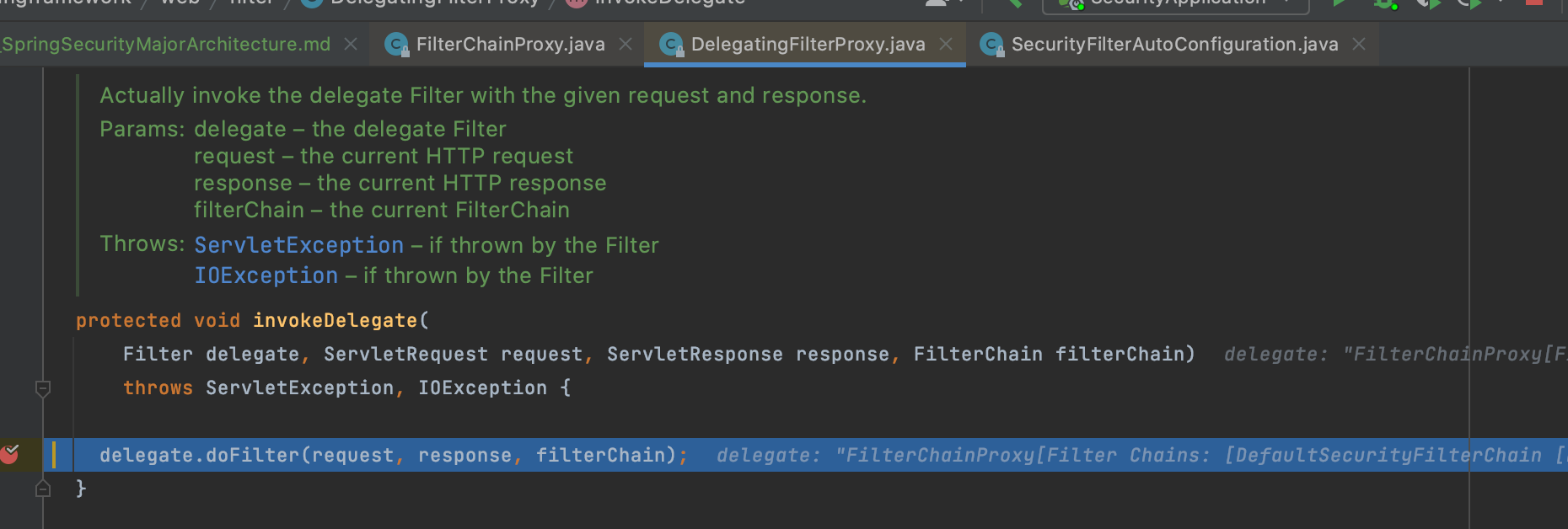
springSecurityFilterChain이 작동(doFilterInternal메서드 안에 VertualFilterChain에서 실제 필터들이 수행됨)
2. 필터 초기화와 다중 보안 설정
- 다중 보안 설정
- 2개 이상의 SecurityConfig 클래스
- 각각의 클래스는 RequestMatcher(Request URL)로 구분하고 순서(@Order)를 설정해야 한다.
- 설정 클래스 별로 필터체인이 생성됨
- 동작 방식
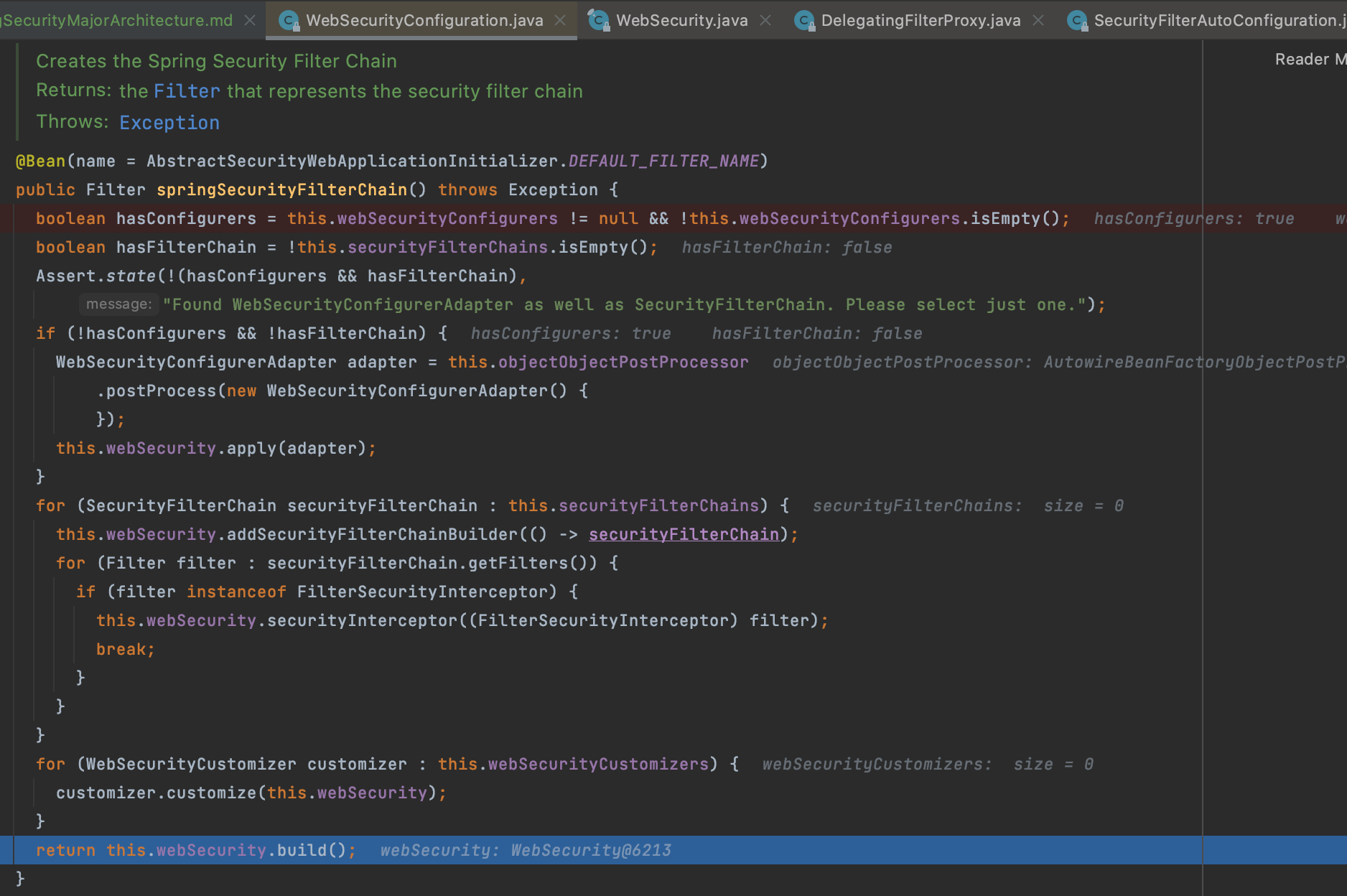
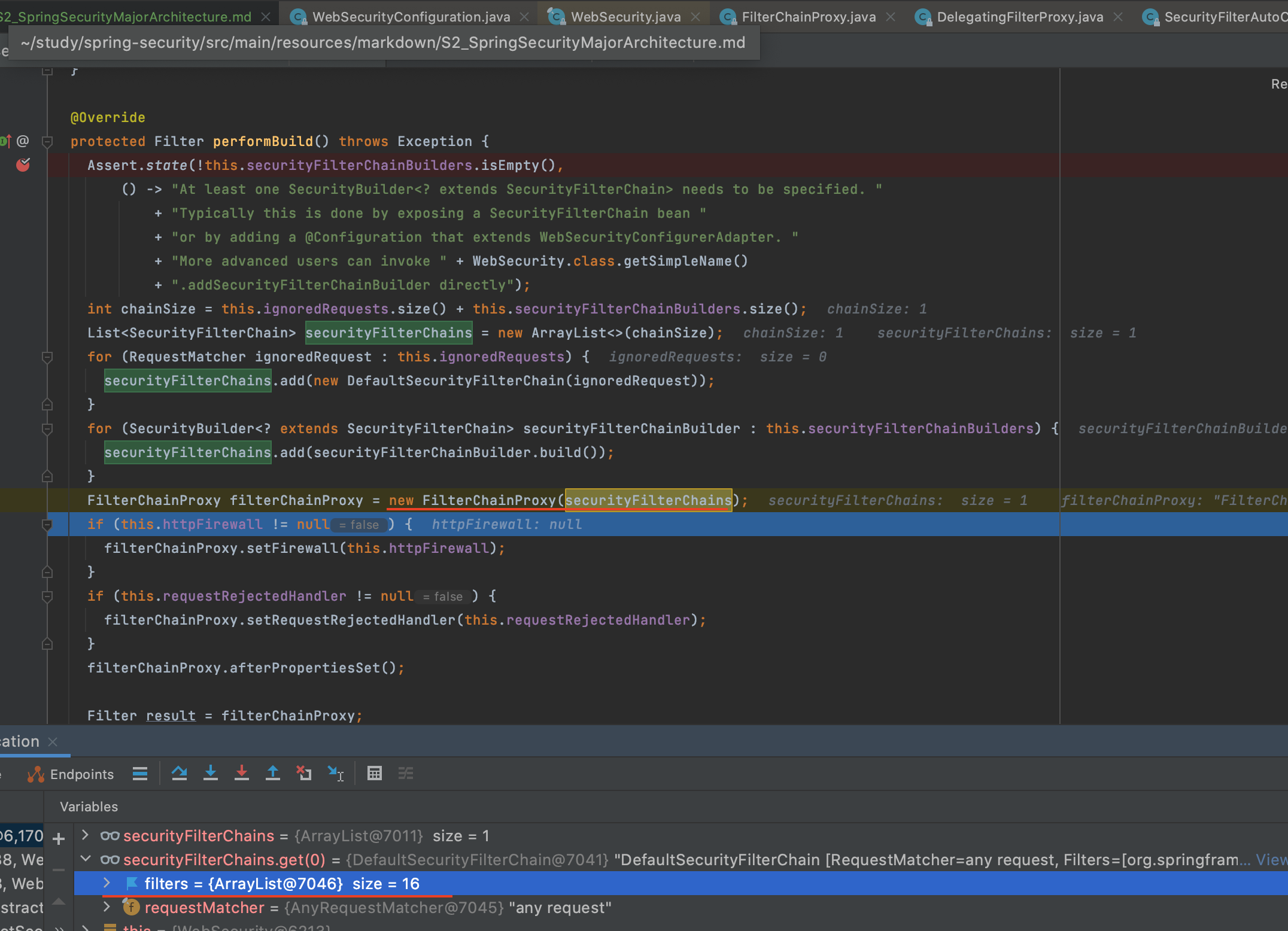
- FilterChainProxy가 여러개의 SecurityFilterChain 객체를 갖는다(SecurityFilterChains)
- 개별 SecurityFilterChain은 Filters(필터정보)와 RequestMatcher(요청정보)를 갖는다.
- FilterChainProxy가 요청을 받으면 요청정보에 맞는 RequestMatcher를 갖는 SecurityFilterChain으로 보안작업을 수행한다.
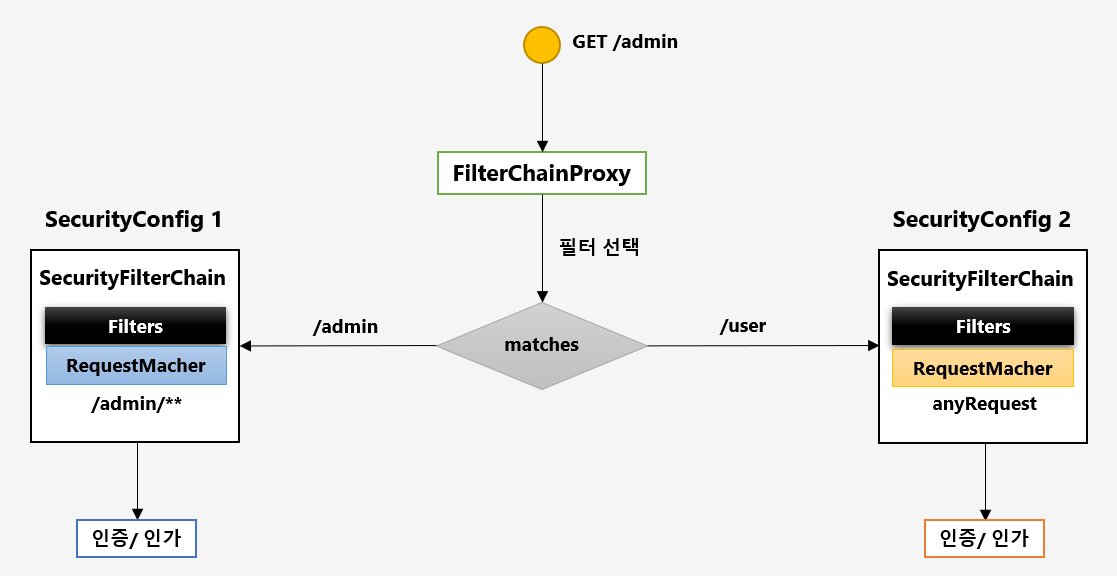
- 테스트
- security1은 인증필요, security2는 permitAll
@Test void needAuthorityConfig() throws Exception { ResultActions needAuthority = mockMvc.perform(get("/security1")); ResultActions permitAll = mockMvc.perform(get("/security2")); assertAll(() -> { needAuthority.andExpect(status().isUnauthorized()); permitAll.andExpect(status().isOk()); }); }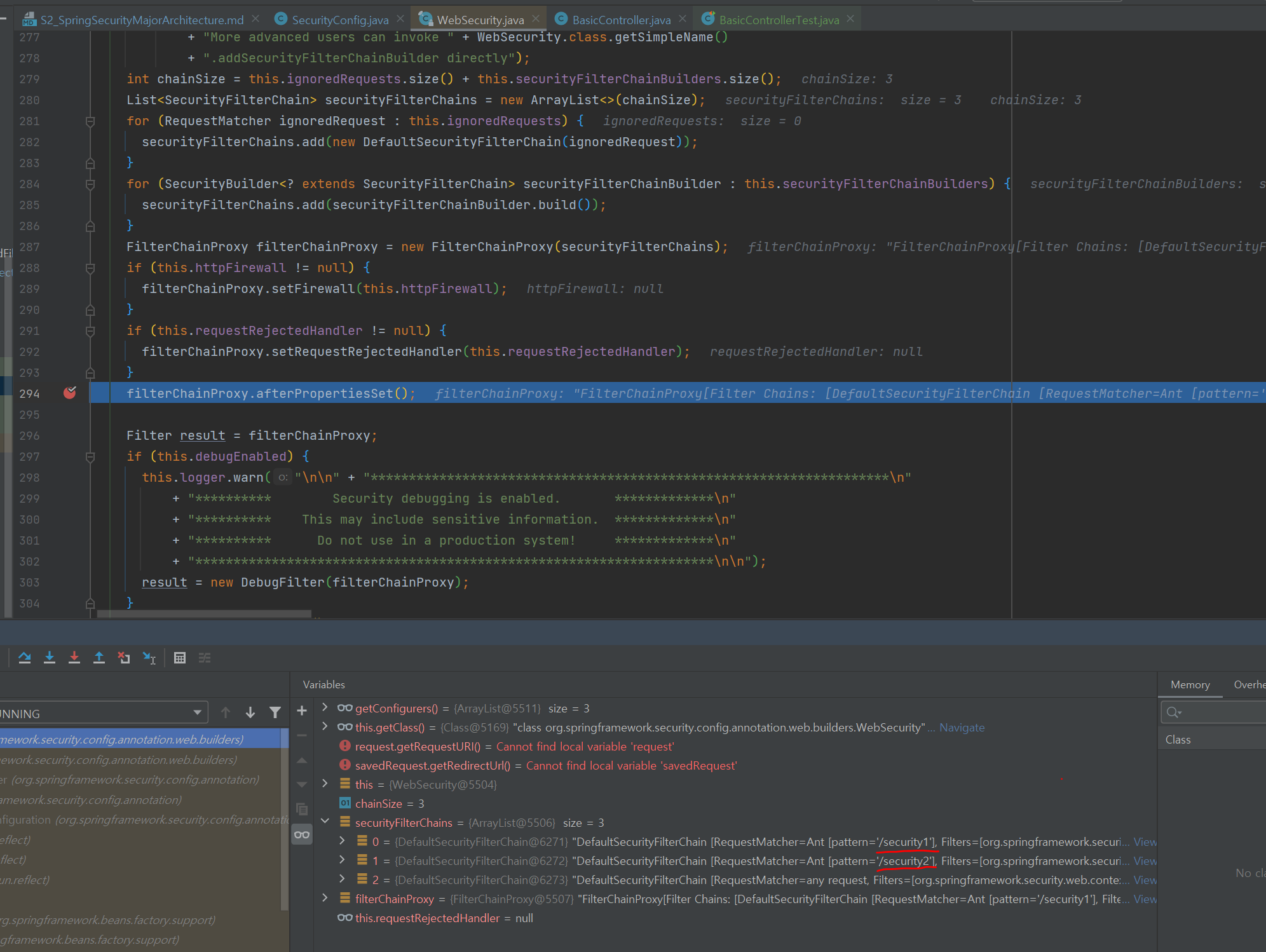
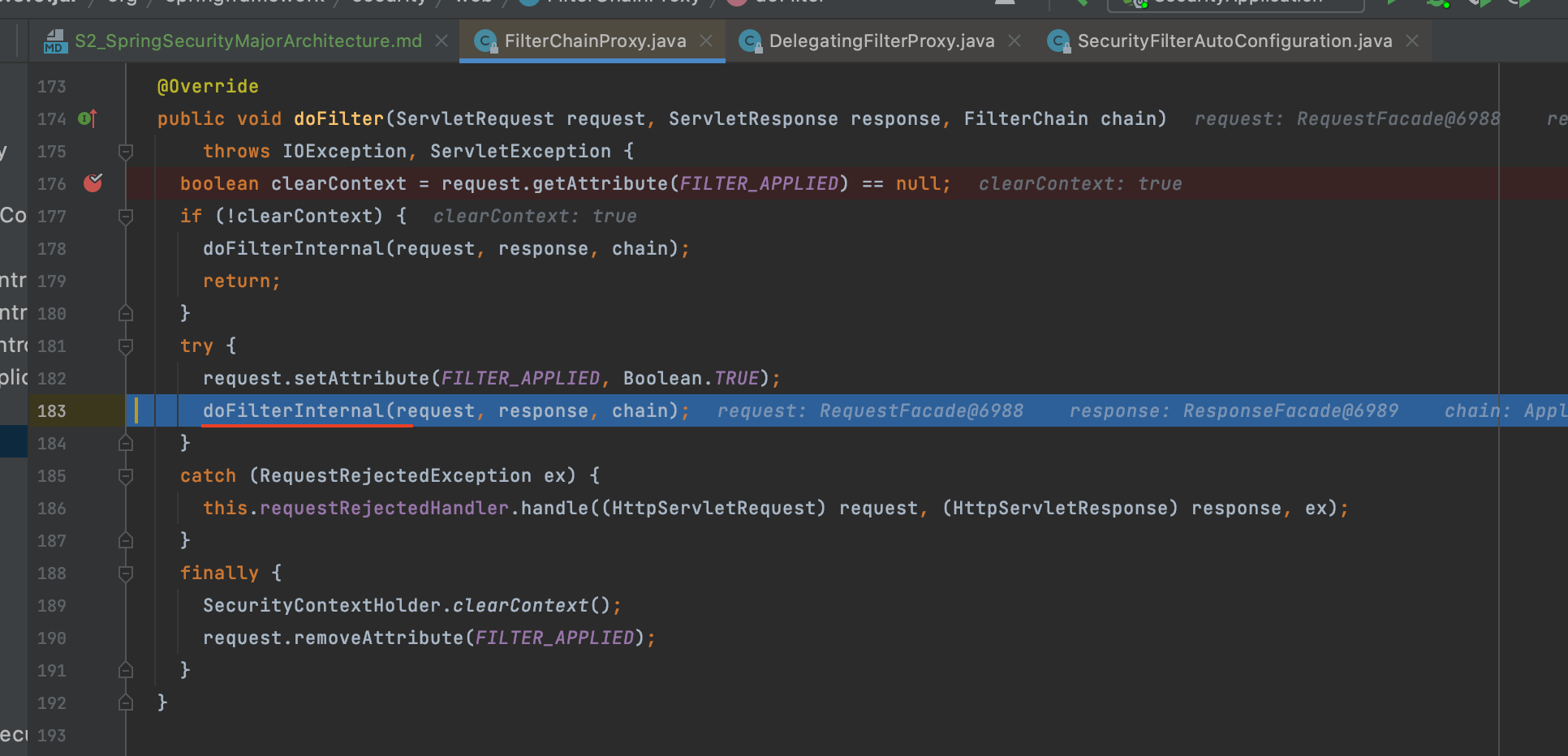
- 필터체인 선정 시점(FilterChainProxy.doFilterInternal)
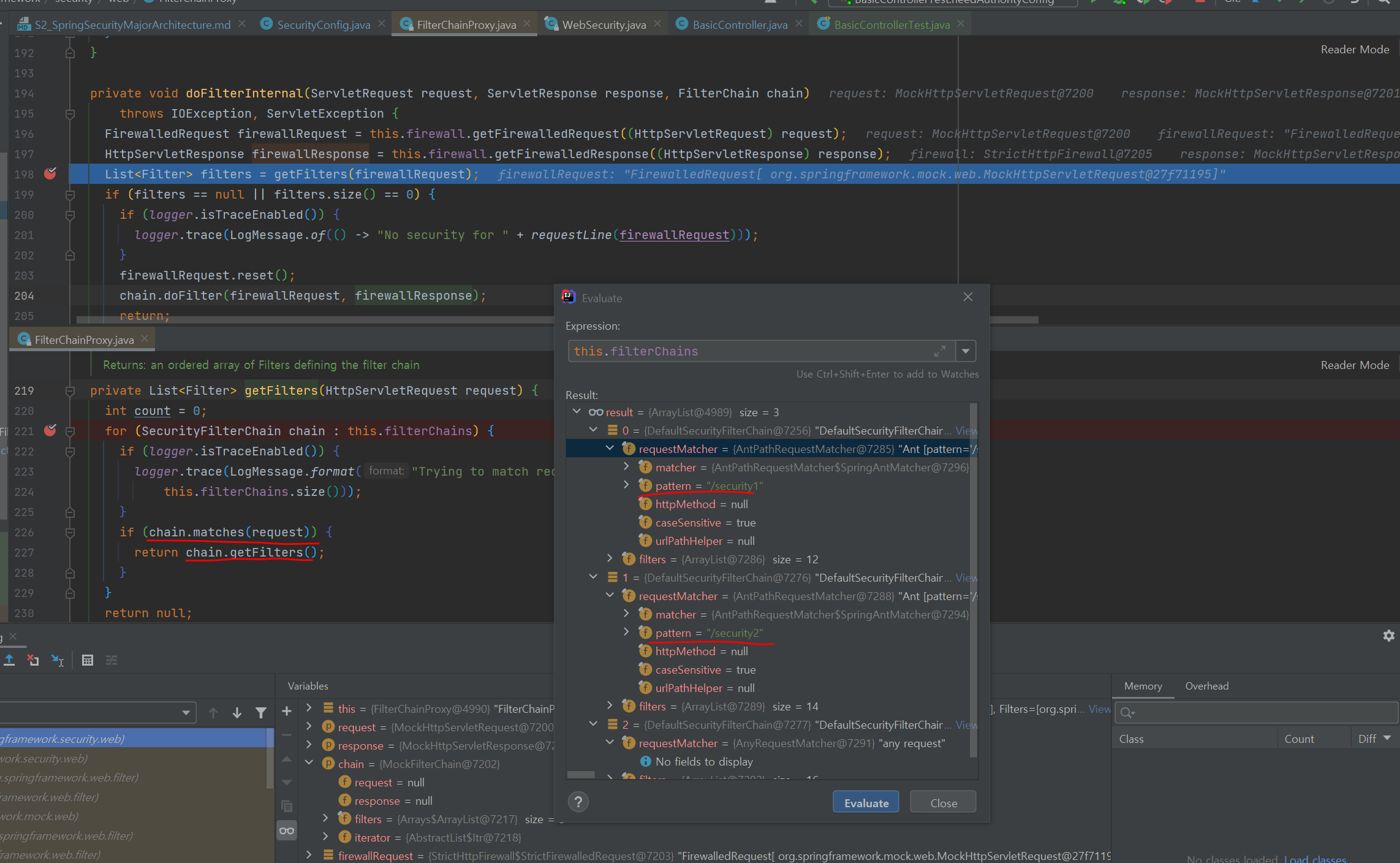
3. Authentication(인증)
- Authentication?
- 사용자가 누구인지 증명하는 것
- 인증 결과는 SecurityContext에 저장되어 전역적으로 참조할 수 있다.
- SpringSecurity에서는 interface이며 그 구현체를 인증정보를 전달하는 객체로 사용한다.
- Authentication 객체가 포함하는 정보
1. principal : 사용자 아이디 혹은 User 객체를 저장 2. credentials : 사용자 비밀번호 3. authorities : 인증된 사용자의 권한 목록 4. details : 인증 부가 정보 5. Authenticated : 인증 여부 - SecurityContext에 저장되기 까지의 과정
1. UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter에서 Authentication 객체 생성 2. 이 때 Authentication principal은 username, credentials는 password(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken은 Authentication 구현체) 3. Authentication 객체 AuthenticationManager로 전달 4. 인증 후 인증객체를 갱신 : principal은 UserDetails, credentials는 null 5. 인증정보를 SecurityContextHolder(ThreadLocal)에 저장
4. 인증 저장소 - SecurityContextHolder, SecurityContext
- SecurityContext
- Authentication 객체가 저장되는 보관소
- 언제든지 Authentication 객체를 꺼내어쓸 수 있도록 제공되는 클래스
- ThreadLocal에 저장되어 어디서나 참조가 가능
- ThreadLocal : 다른 스레드에서는 접근할 수 없는 개별 Thread의 저장소
- SecurityContextHolder
- SecurityContext를 갖고있는 클래스
- SecurityContext 저장 방식
1. MODE_THREADLOCAL : 하나의 스레드 당 하나의 SecurityContext 객체를 할당(default) 2. MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL : 메인 스레드와 자식 스레드에 대해 동일한 SecurityContext를 유지 3. MODE_GLOBAL : 응용 프로그램에서 단 하나의(static) SecurityContext를 갖는다.- 인증이 완료되면 저장방식에 따라 ThreadLocal에 인증정보를 저장하고 HttpSession에 SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT로도 저장.
- 인증 후에 다시 접속할 때에는 session에 저장돼있던 SecurityContext를 가져온다.
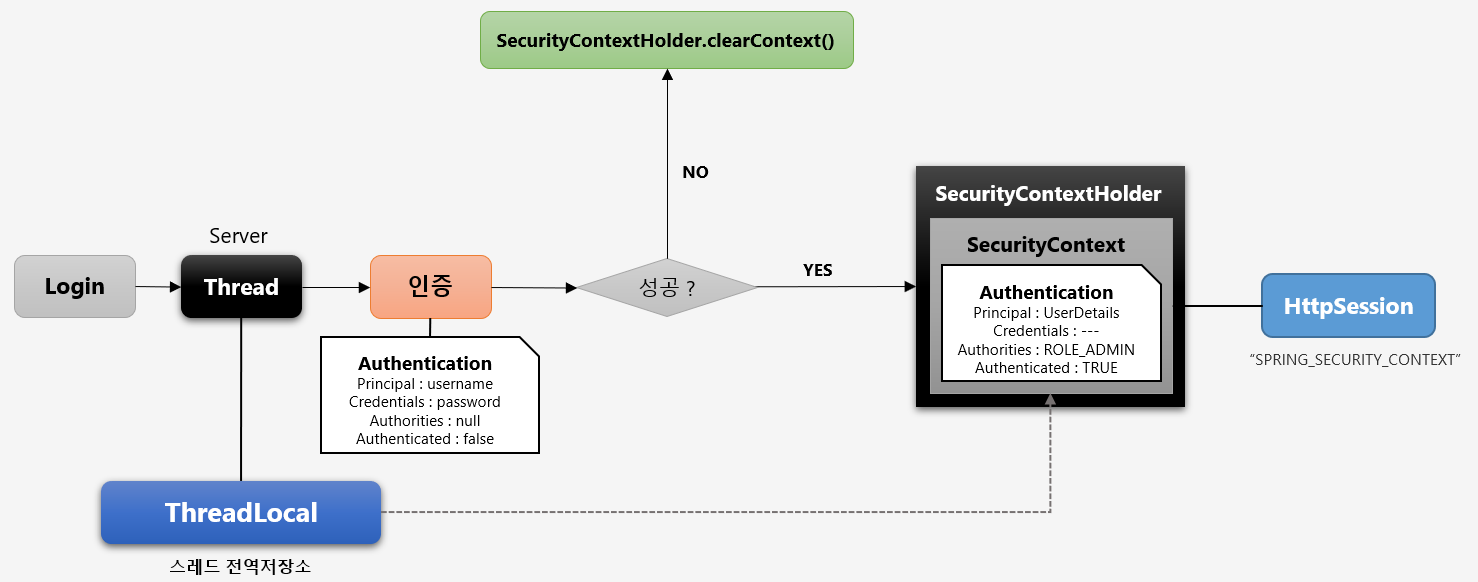
5. SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
- SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
- SecurityContext 객체의 생성, 저장, 조회 처리 역할
동작 순서 - 새로운 SecurityContext 생성하여 SecurityContextHolder에 저장 - 인증이 완료되면 Authentication 객체를 SecurityContext에 저장 - 익명 사용자가 아닌 경우 Session에 SecurityContext 저장 - 인증이 완료된 이후 다른 request가 들어오면 Session에서 SecurityContext를 꺼내어 SecurityContextHolder에 저장 - SecurityContext안에 Authentication 객체가 존재하면 계속 인증을 유지한다.- 동작 코드
- SecurityContext를 Session에서 가져오는데 없으면 만들어준다.
- finally에서 clear하고 session에 저장한다.
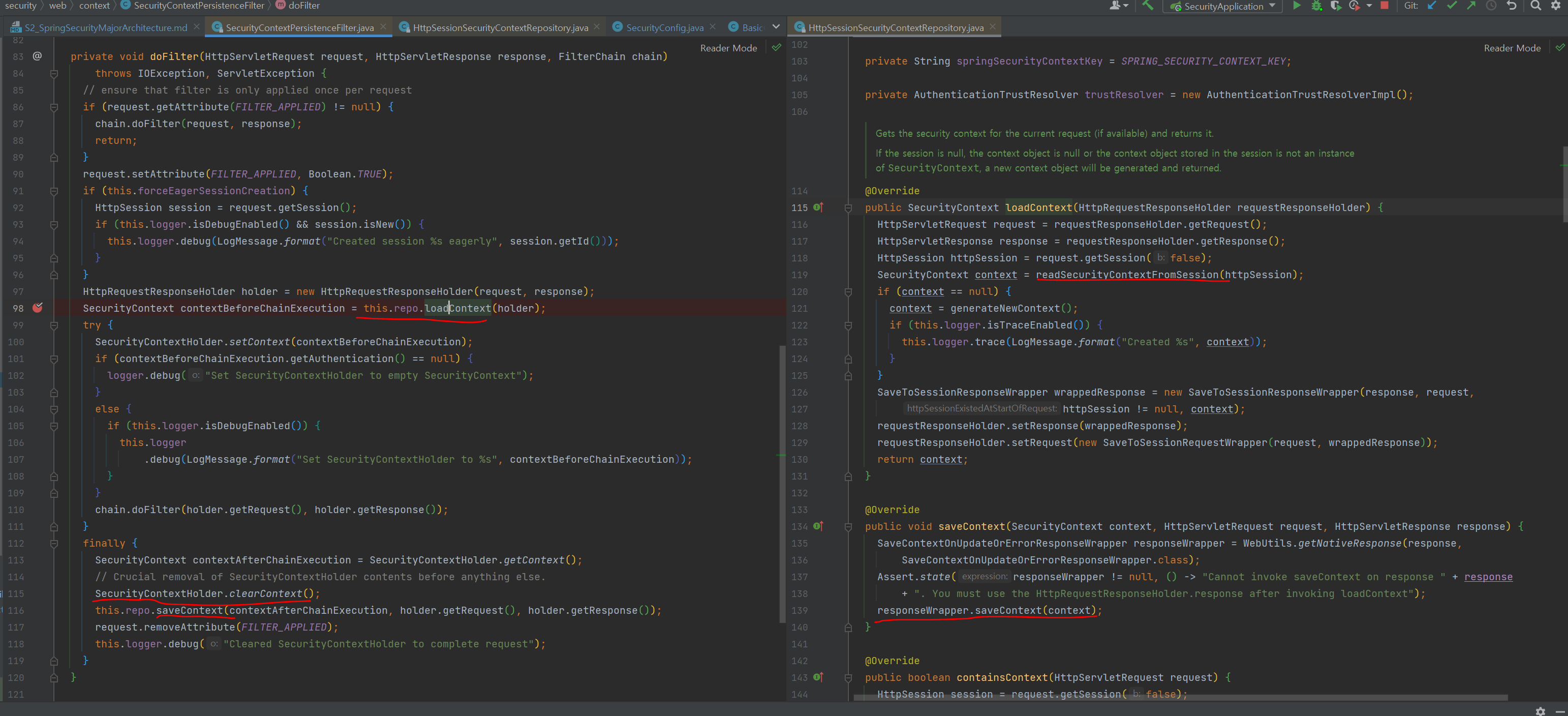
6. 인증 흐름 이해 AuthenticationFlow
- 인증 흐름
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter : 매니저로부터 받은 인증객체 SecurityContext에 저장 (AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter.successfulAuthentication)
- AuthenticationManager : 인증의 전반적인 관리(위임, 토큰 객체 생성 등), 실제 인증 역할은 AuthenticationProvider에 위임
- AuthenticationProvider : 실제 인증 처리, 유저 유효성 검증(패스워드 체크 등)
- UserDetailsService : 유저 객체 조회, UserDetails타입으로 반환
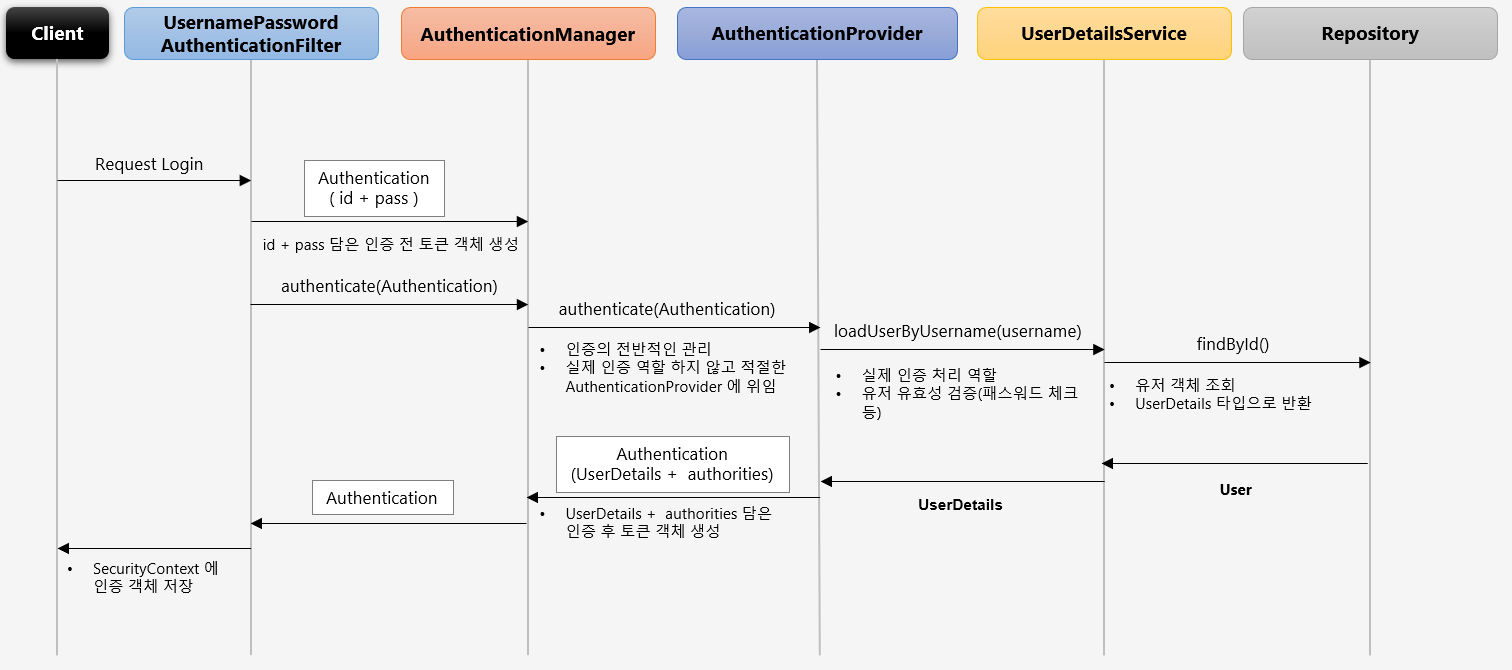
7. AuthenticationManager
- AuthenticationManager
- interface이며, 기본 구현체는 ProviderManager
- 인증처리는 Provider에게 위임
- 선택하는 Provider는 인증 요청에 따라 다름(Form, RememberMe, Oauth)
- 인증 요청에 적합한 Provider가 없는 경우 parent 필드에 적합한 Provider가 있는지 탐색해서 사용
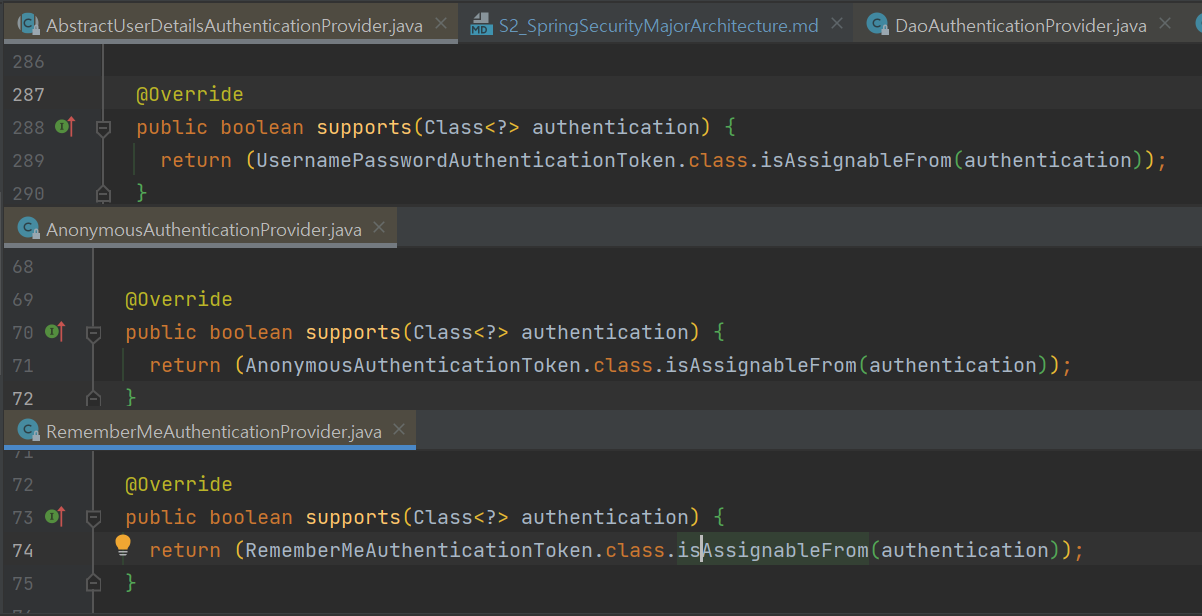
- 적합한지 아닌지는 Provider의 supports메서드 사용
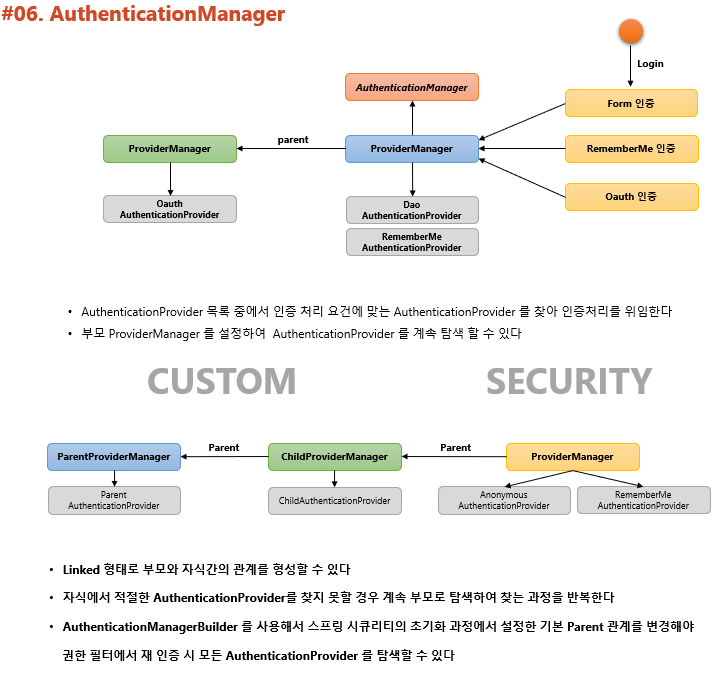
- 초기화 과정
- AuthenticationManagerBuilder에서 AuthenticationProvider를 추가함
- 여러 개를 만들어 authenticationProviders에 add
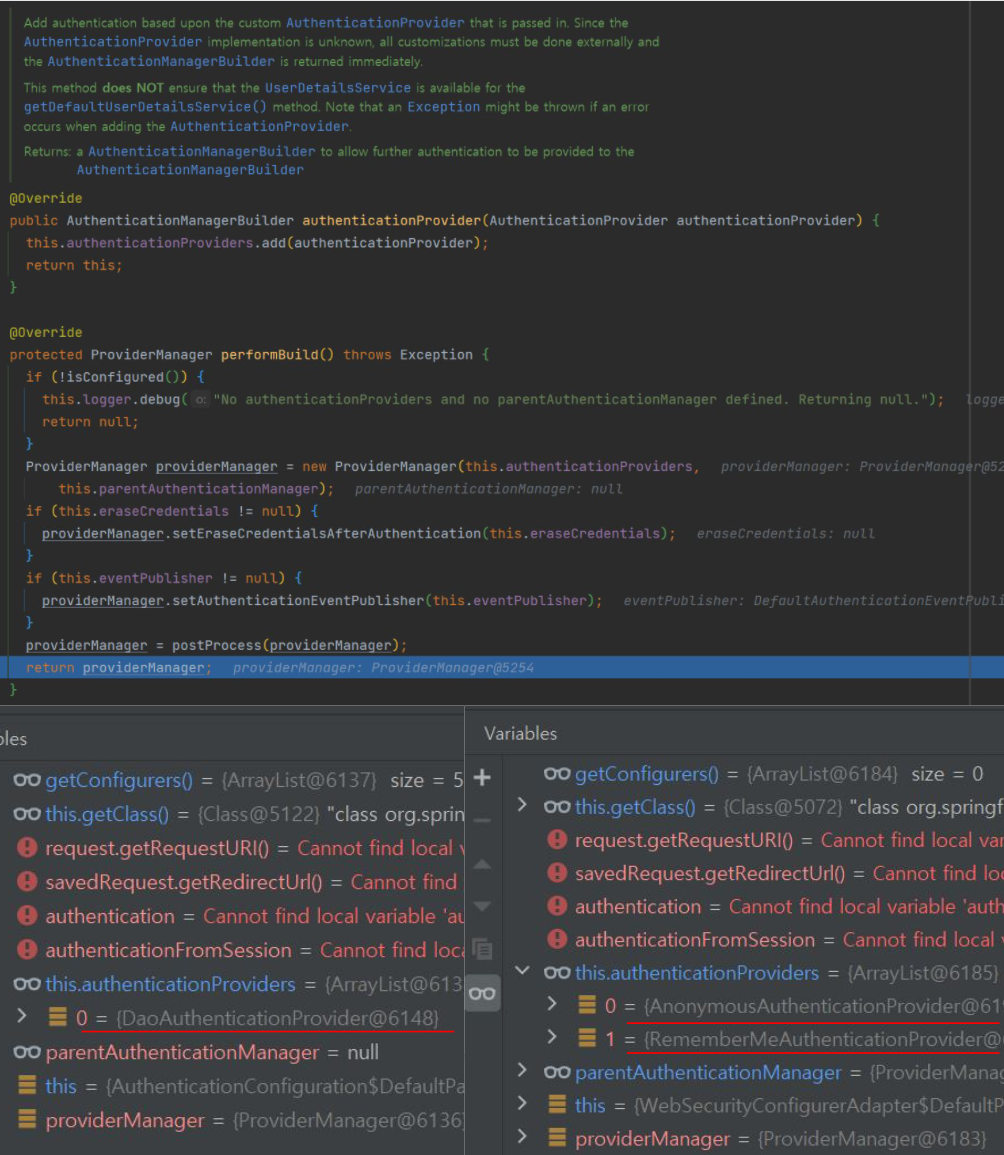
- 동작
- 초기화 과정에서 결정된 Provider에게 인증 위임
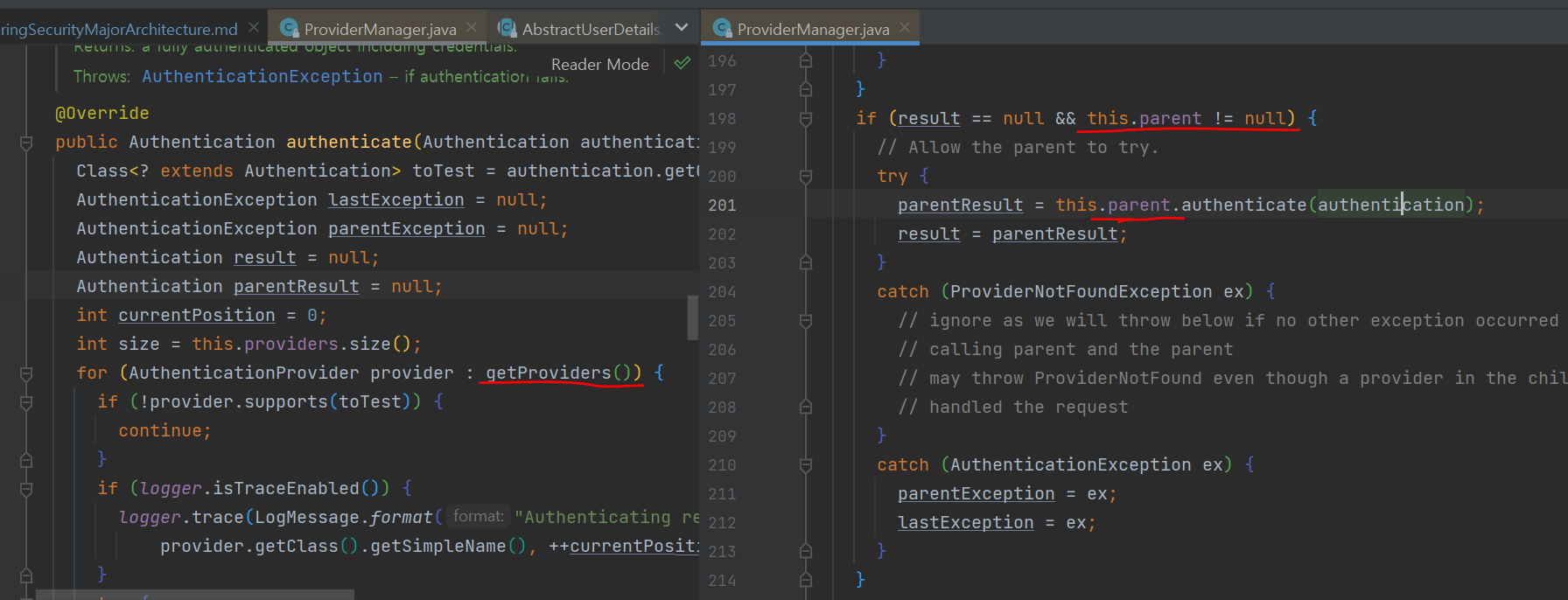
- 적합 Provider인지 아닌지는 Provider의 supports메서드 사용해서 판단
- 인증 객체 인스턴스 타입에 따라 선택
- 작업이 완료되면 AuthenticationManager를 호출한 Filter로 인증 객체를 리턴
- 초기화 과정에서 결정된 Provider에게 인증 위임
8. Authorization
- 인가 : 접근이 허가된 권한을 갖는 사용자인지 입증하는 절차
웹 계층 : URL요청에 따른 화면 단위의 보안(ex_ GET /user/id01) 서비스 계층 : 메서드 기능 단위의 보안 (ex_ public void getUserByUsername()) 도메인 계층 : 객체 단위의 보안- FilterSecurityInterceptor
- 필터 체인 마지막에 위치한 필터
public class FilterSecurityInterceptor extends AbstractSecurityInterceptor implements Filter { ... }- 인증된 사용자의 요청에 대해 승인/거부 여부를 최종적으로 결정
- 권한 처리는 AccessDecisionManager에 위임
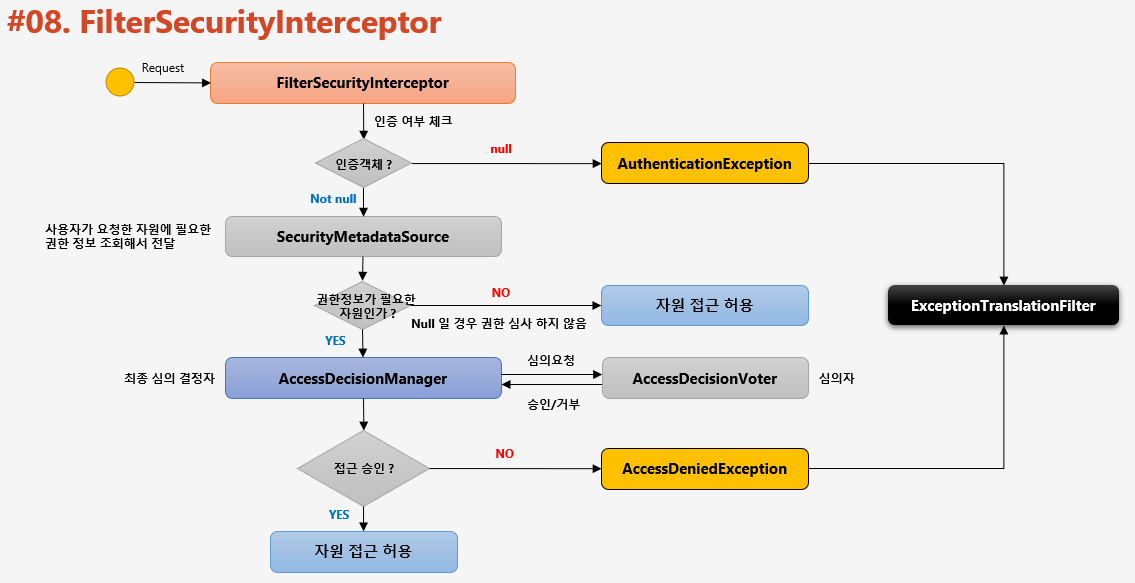
- FilterSecurityInterceptor에서 super클래스의 beforeInvocation호출
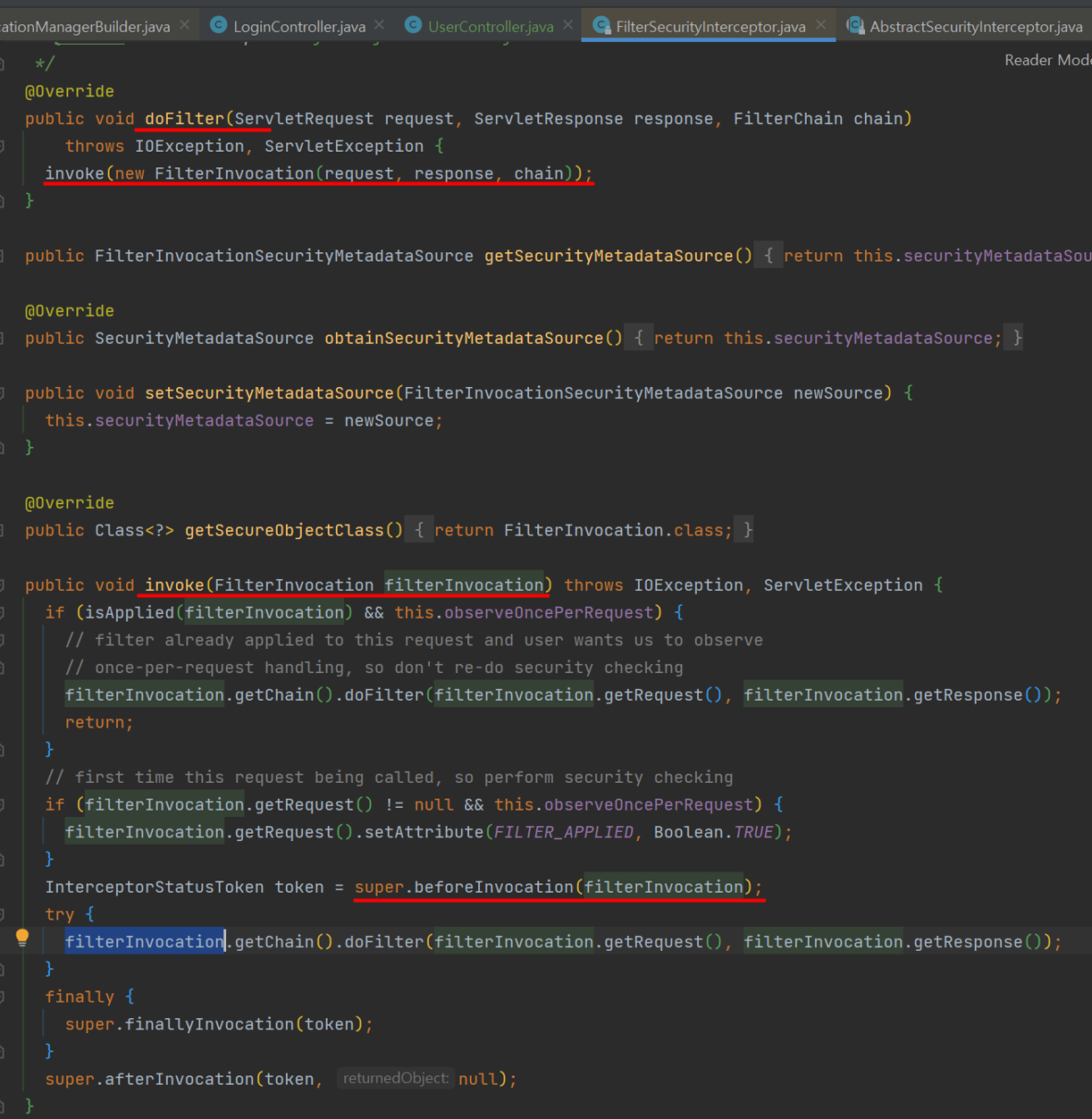
- beforeInvocation : 메타데이터 활용해서 인가처리(AbstractSecurityInterceptor)
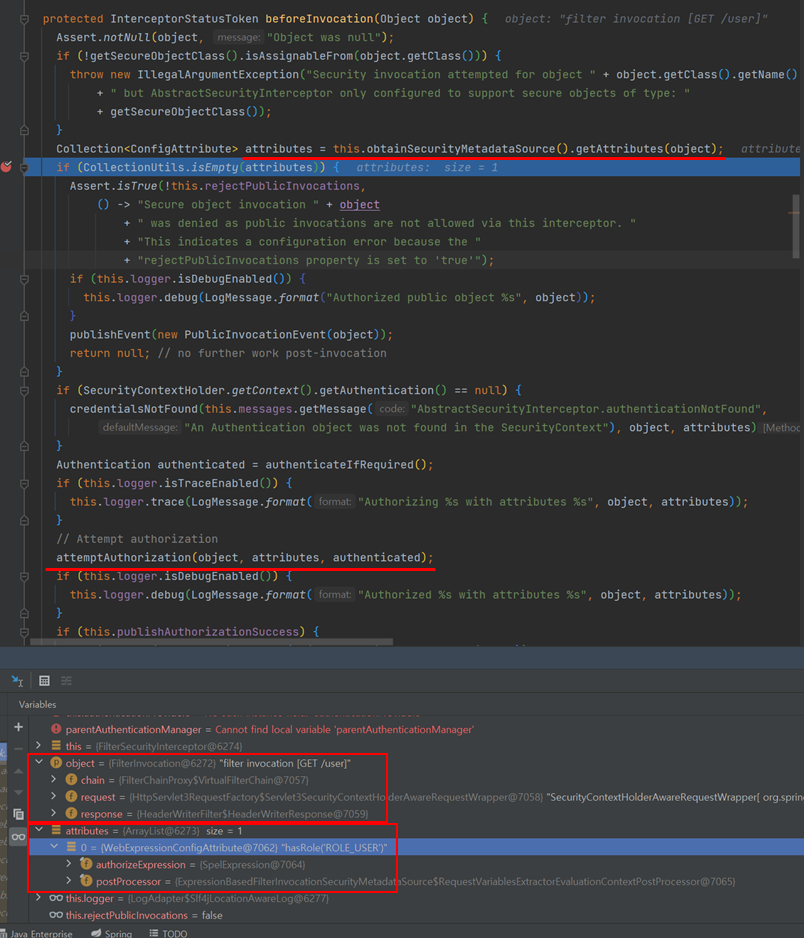
- attemptAuthorization : AffirmativeBased가 인가 결정
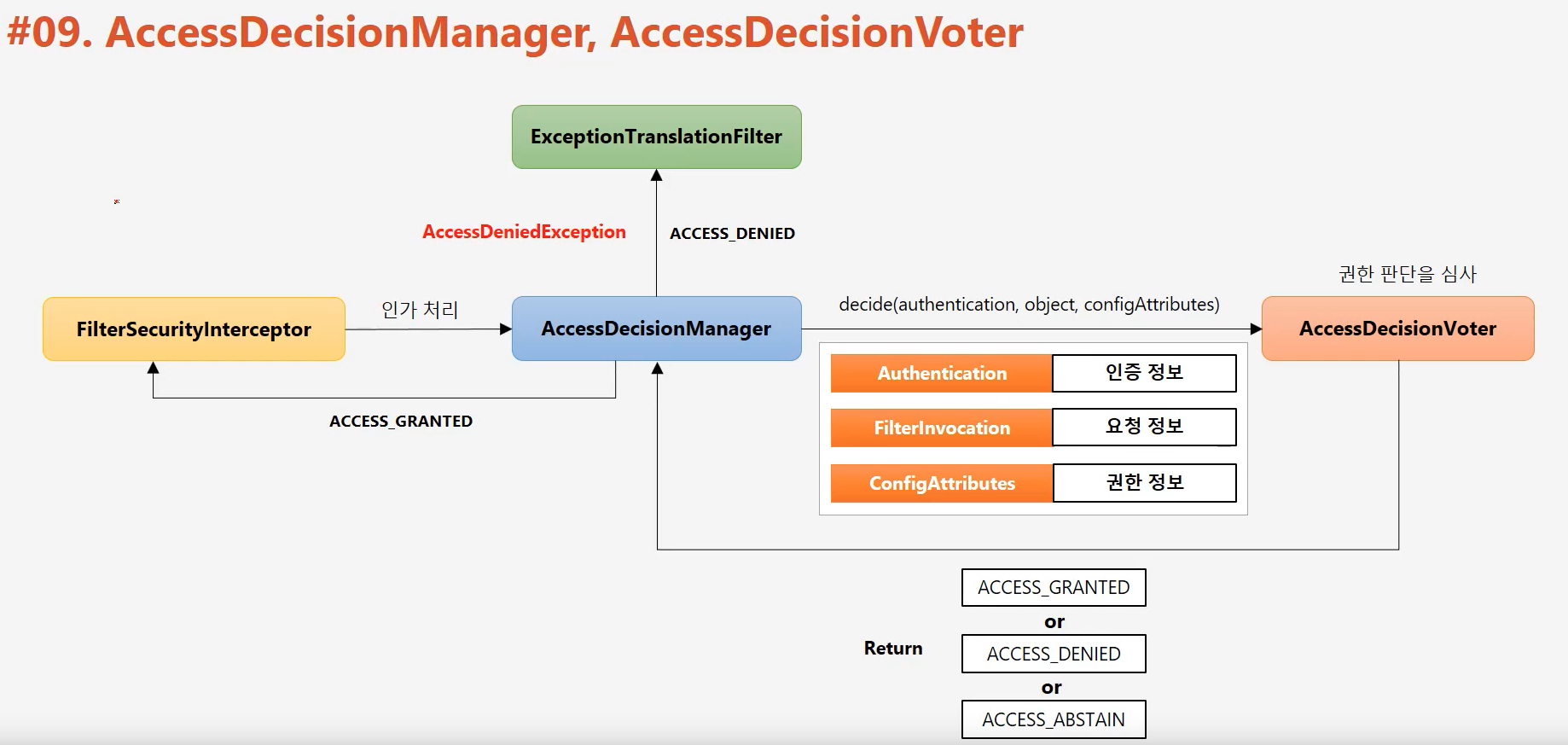
9. 인가결정 심의자
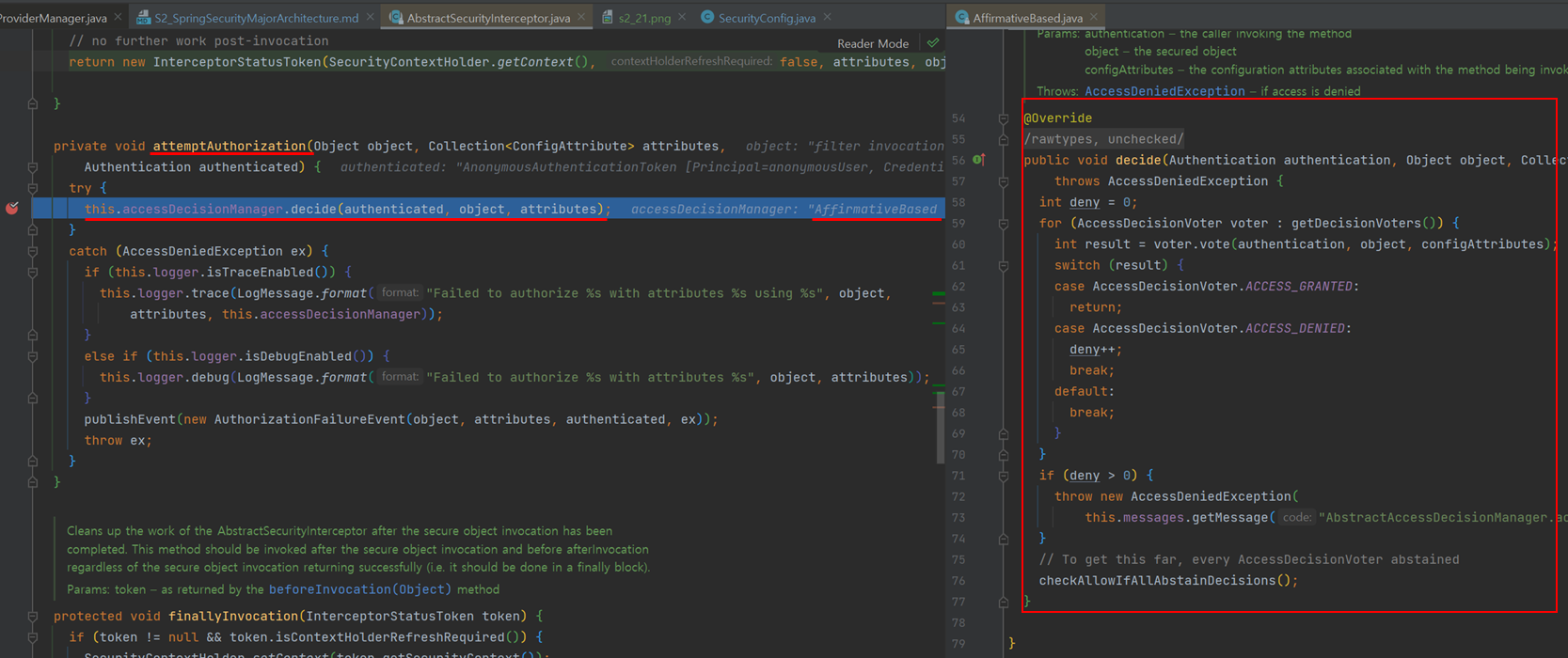
- AccessDecisionManager
- 사용자의 자원접근 허용여부를 최종 결정하는 주체
- 여러 개의 Voter를 가지며 Voter들은 접근허용, 거부, 보류에 해당하는 각각의 값을 리턴한다.
- 접근결정의 세 가지 유형
- AffirmativeBased : 하나라도 접근 허가면 허가
- ConsensusBased : 다수표에의해 최종허가 판단. 동수일 경우 allowIfEqualGrantedDeniedDecisions옵션에 따름(default = 허가)
- UnanimousBased : 만장일치여야만 승인
- AccessDecisionVoter
- 판단을 심사하는 주체
- 권한 부여의 판단 근거가 되는 자료
- Authentication : 인증정보
- FilterInvocation : 요청정보(antManager("/user"))
- ConfigAttributes : 권한정보(hasRole("USER"))
- 구조
- FilterSecurityInterceptor가 AccessDecisionManager에 인가처리를 요청하면?
- AccessDecisionManager가 갖는 Voter들이 판단처리
- 승인이 거부되면 ExceptionTranslationFilter가 처리
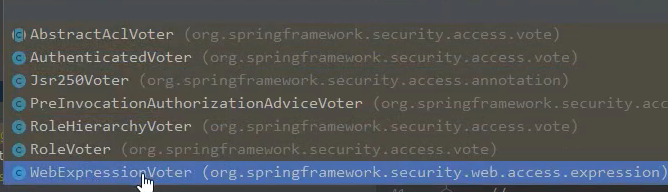
- AccessDecisionVoter의 여러 구현체들
10. 정리
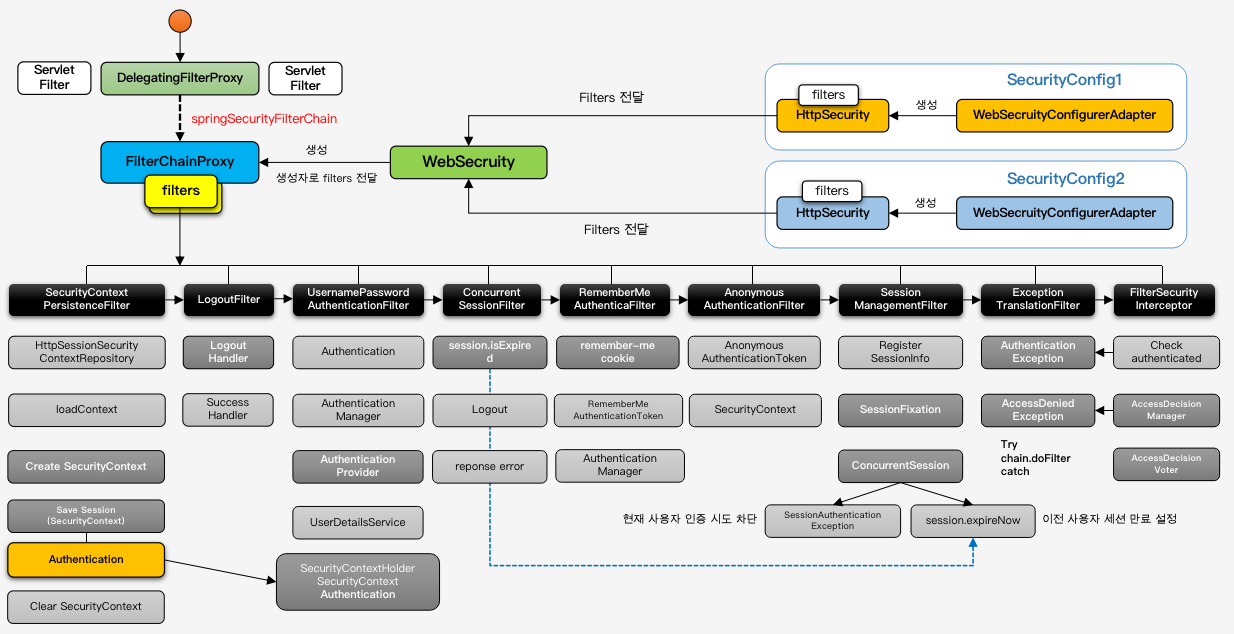
- 초기화
- SecurityConfig 선언
- 선언된 대로 HttpSecurity가 filter들을 생성
- WebSecurity가 HttpSecurity들의 filter목록을 받아 FilterChainProxy로 전달
- DelegatingFilterProxy가 초기화될 때 springSecurityFilterChain이라는 빈을 찾아서 요청을 위임하게됨
- springSecurityFilterChain빈은 FilterChainProxy
- 인증 인가 과정 : 로그인 시도 - 성공
- SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
- SecurityContext가 있는지 확인
- 있으면 가져오고 없으면 만들어줌
- LogoutFilter : 로그아웃 요청이 아니므로 패스
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
- 인증처리하고 SecurityContext에 인증객체 저장
- AuthenticationManager, AuthenticationProvider, UserDetailsService
- 인증에 성공하면 SessionManagementFilter에 선언된 기능을 사용해서 후속처리
- LoginSuccessHandler에 따라 동작하게됨
- SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
- 이 전에 로그인한 정보를 가져옴
- LogoutFilter : 로그아웃 요청이 아니므로 패스
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter : 인증 요청이 아니므로 패스
- ConcurrentSessionFilter : 동시세션제어가 아니므로 패스
- RememverMeAuthenticationFilter : remember-me cookie 확인
- AnonymousAuthenticationFilter : 인증사용자이므로 패스
- SessionManagementFilter : 세션이 있고 세션에 인증객체도 있기 때문에 패스
- ExceptionTranslationFilter : 인가예외 처리
- FilterSecurityInterceptor : 인가처리를 하는 필터로 예외발생시킴
1,2,3,4 : 로그인 요청 5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 : 자원접근 요청
- SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
'공부 > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring Security(3) - form 로그인 방식 예제 (0) | 2021.07.12 |
|---|---|
| Spring Security(1) (0) | 2021.06.17 |
| 토비의 스프링(8) - 스프링이란 무엇인가? (0) | 2021.06.17 |
| 토비의스프링(7) - 스프링 핵심 기술의 응용 (0) | 2021.06.17 |
| 토비의스프링(6) - AOP (0) | 2021.03.30 |
Comments